Discover The Ultimate Guide To WPD TB: Expert Tips And Insights
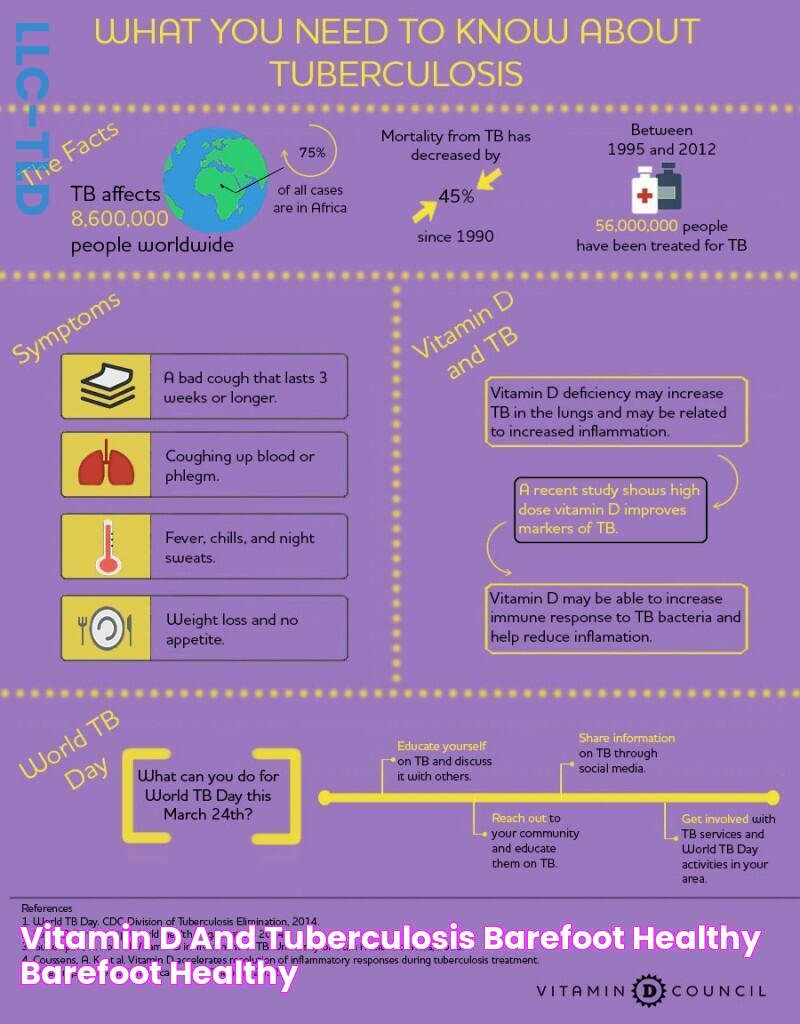
WPD TB is a keyword term used to describe a specific type of tuberculosis (TB) caused by _Mycobacterium tuberculosis_ bacteria. It is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that primarily affects the lungs.
WPD TB is a major public health concern, particularly in developing countries. It is one of the leading causes of death from infectious diseases worldwide. The disease is spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. People who are in close contact with an infected person are at the highest risk of becoming infected.
The symptoms of WPD TB can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue. In severe cases, WPD TB can lead to lung damage, respiratory failure, and even death.
Read also:Your Trusted Funeral Home In Gainesville Tx Compassionate Care
The diagnosis of WPD TB is based on a combination of clinical symptoms, a physical examination, and laboratory tests. Treatment for WPD TB typically involves a combination of antibiotics and other medications. Treatment can be lengthy and complex, but it is essential to prevent serious complications and death.
WPD TB
WPD TB is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. It primarily affects the lungs and is a major public health concern, particularly in developing countries.
- Airborne: WPD TB is spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Bacteria: It is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Cough: A persistent cough is a common symptom of WPD TB.
- Lungs: WPD TB primarily affects the lungs.
- Public health: WPD TB is a major public health concern, particularly in developing countries.
- Tuberculosis: WPD TB is a type of tuberculosis.
- World Health Organization: The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 10 million people developed TB in 2020.
These key aspects highlight the importance of WPD TB as a global health issue. The airborne nature of the disease makes it easily transmissible, and the impact on the lungs can lead to severe respiratory complications. The World Health Organization (WHO) plays a crucial role in coordinating global efforts to prevent, diagnose, and treat WPD TB, particularly in resource-limited settings.
1. Airborne
The airborne nature of WPD TB is a critical aspect of its transmission and prevention. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, tiny droplets containing the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis are released into the air. These droplets can remain suspended in the air for several hours, and they can be inhaled by other people who are in close contact with the infected person.
The airborne transmission of WPD TB makes it a highly contagious disease. People who spend extended periods of time in close contact with an infected person, such as family members, healthcare workers, and coworkers, are at the highest risk of becoming infected.
Understanding the airborne transmission of WPD TB is essential for preventing the spread of the disease. Public health measures, such as isolation of infected individuals, proper ventilation, and the use of face masks, can help to reduce the risk of transmission.
Read also:Before The Transformation Heidi Montags Journey Presurgery
In addition, early diagnosis and treatment of WPD TB is crucial to prevent the spread of the disease. People who have symptoms of WPD TB, such as a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, and weight loss, should seek medical attention promptly.
2. Bacteria
The bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the causative agent of WPD TB. It is a type of bacteria that primarily infects the lungs, causing inflammation and tissue damage. The bacteria can also spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, bones, and kidneys.
Understanding the role of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in WPD TB is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. Public health measures, such as vaccination and early detection, are essential to control the spread of the disease.
In addition, the development of new antibiotics and other drugs is critical to combat drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Research and innovation are ongoing to find more effective ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat WPD TB.
3. Cough
A persistent cough is one of the most common symptoms of WPD TB. It is caused by the inflammation and irritation of the airways and lungs caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. The cough may be dry or productive, and it may be accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue.
Coughing is an important defense mechanism that helps to clear the airways of mucus and other irritants. However, a persistent cough can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as WPD TB. It is important to seek medical attention if you have a cough that lasts for more than two weeks, or if you have other symptoms of WPD TB.
Early diagnosis and treatment of WPD TB is essential to prevent serious complications, such as lung damage, respiratory failure, and death. If you have a persistent cough, your doctor may order a chest X-ray or other tests to rule out WPD TB and other medical conditions.
4. Lungs
WPD TB primarily affects the lungs, causing inflammation and damage to the lung tissue. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue. In severe cases, WPD TB can lead to lung damage, respiratory failure, and even death.
- Respiratory system: WPD TB is a respiratory disease that primarily affects the lungs. The bacteria causing WPD TB can be inhaled into the lungs, where it can cause inflammation and damage to the lung tissue.
- Immune system: WPD TB can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off other infections. This can lead to a range of complications, including pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis.
- Transmission: WPD TB is spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. People who are in close contact with an infected person are at the highest risk of becoming infected.
- Treatment: WPD TB is treated with a combination of antibiotics and other medications. Treatment can be lengthy and complex, but it is essential to prevent serious complications and death.
Understanding the connection between WPD TB and the lungs is crucial for preventing, diagnosing, and treating the disease. Public health measures, such as vaccination and early detection, are essential to control the spread of the disease. In addition, the development of new antibiotics and other drugs is critical to combat drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
5. Public health
The connection between public health and WPD TB is significant. WPD TB is a major public health concern, particularly in developing countries, due to its high prevalence and the challenges associated with prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Transmission and spread: WPD TB is spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. This makes it a highly contagious disease, and it can spread rapidly in crowded and poorly ventilated areas. In developing countries, where access to healthcare and public health services may be limited, the spread of WPD TB can be particularly problematic.
- Vulnerable populations: People living in poverty and marginalized communities are at a higher risk of developing WPD TB. This is due to a combination of factors, including poor nutrition, lack of access to healthcare, and inadequate housing conditions. In developing countries, where poverty is widespread, a large proportion of the population may be vulnerable to WPD TB.
- Limited resources: Developing countries often have limited resources to allocate to public health programs, including those aimed at preventing and treating WPD TB. This can lead to a lack of access to diagnostic tests, medications, and other essential services. As a result, WPD TB can go undiagnosed and untreated, leading to the spread of the disease and the development of drug-resistant strains.
- Global impact: WPD TB is not just a problem in developing countries. It is a global health threat, and it can spread to any country, regardless of its level of development. The movement of people across borders can contribute to the spread of WPD TB, and it is important for all countries to have strong public health systems in place to prevent and control the disease.
Addressing the public health challenges associated with WPD TB requires a multi-faceted approach, including improved access to healthcare, increased funding for public health programs, and the development of new strategies for prevention and treatment. By working together, we can help to reduce the burden of WPD TB and improve the health of people around the world.
6. Tuberculosis
WPD TB is a type of tuberculosis (TB) caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB is a serious infectious disease that primarily affects the lungs, and it is one of the leading causes of death from infectious diseases worldwide.
- Transmission
WPD TB is spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. People who are in close contact with an infected person are at the highest risk of becoming infected.
- Symptoms
The symptoms of WPD TB can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue.
- Diagnosis
The diagnosis of WPD TB is based on a combination of clinical symptoms, a physical examination, and laboratory tests. A chest X-ray can be used to identify abnormalities in the lungs, and a sputum test can be used to detect the presence of the bacteria.
- Treatment
The treatment for WPD TB typically involves a combination of antibiotics and other medications. Treatment can be lengthy and complex, but it is essential to prevent serious complications and death.
Understanding the connection between WPD TB and tuberculosis is crucial for preventing, diagnosing, and treating the disease. Public health measures, such as vaccination and early detection, are essential to control the spread of the disease. In addition, the development of new antibiotics and other drugs is critical to combat drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
7. World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is the leading international organization for public health. One of its main goals is to combat tuberculosis (TB), a serious infectious disease that primarily affects the lungs. According to the WHO, an estimated 10 million people developed TB in 2020, making it one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide. WPD TB is a type of TB caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is a major public health concern, particularly in developing countries.
The connection between the WHO's estimate of TB cases and WPD TB is significant. The WHO's data provides a global perspective on the burden of TB, including WPD TB. This information is essential for public health officials and policymakers to develop strategies for preventing and controlling TB. The WHO also provides technical guidance and support to countries in their efforts to combat TB.
For example, the WHO recommends that all people with suspected TB be tested for WPD TB. This is because WPD TB is a more severe form of TB that requires longer and more intensive treatment. The WHO also recommends that people with WPD TB be treated with a combination of antibiotics for at least six months.
The WHO's work on TB is essential for reducing the burden of this disease worldwide. The organization's data, guidance, and support help countries to prevent, diagnose, and treat TB, including WPD TB.
Frequently Asked Questions about WPD TB
This section provides answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about WPD TB, a serious type of tuberculosis caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Question 1: What is the difference between WPD TB and other types of TB?
Answer: WPD TB is a type of TB that primarily affects the lungs. It is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Other types of TB can affect other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, bones, and kidneys.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of WPD TB?
Answer: The symptoms of WPD TB can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue. In severe cases, WPD TB can lead to lung damage, respiratory failure, and even death.
Question 3: How is WPD TB diagnosed?
Answer: WPD TB is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical symptoms, a physical examination, and laboratory tests. A chest X-ray can be used to identify abnormalities in the lungs, and a sputum test can be used to detect the presence of the bacteria.
Question 4: How is WPD TB treated?
Answer: WPD TB is treated with a combination of antibiotics and other medications. Treatment can be lengthy and complex, but it is essential to prevent serious complications and death.
Question 5: Can WPD TB be prevented?
Answer: There is no vaccine that is fully effective against WPD TB. However, there are some preventive measures that can be taken, such as avoiding close contact with people who are infected with TB, getting tested for TB if you have symptoms, and taking medication to prevent TB if you are at high risk of developing the disease.
Question 6: What is the prognosis for people with WPD TB?
Answer: The prognosis for people with WPD TB depends on the severity of the infection and how early it is diagnosed and treated. With early diagnosis and treatment, most people with WPD TB can be cured. However, if the infection is severe or it is not treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications and even death.
Summary: WPD TB is a serious type of tuberculosis that can have serious consequences if it is not diagnosed and treated promptly. However, with early diagnosis and treatment, most people with WPD TB can be cured.
Next steps: If you have any questions about WPD TB, please speak to your doctor or other healthcare provider.
Tips for Preventing and Managing WPD TB
WPD TB is a serious type of tuberculosis that can have serious consequences if it is not diagnosed and treated promptly. However, there are a number of things you can do to prevent and manage WPD TB, including:
Tip 1: Get vaccinated against TB.
The TB vaccine is not 100% effective, but it can help to protect you from developing WPD TB. The vaccine is recommended for people who are at high risk of developing TB, such as people who live in or travel to areas where TB is common.
Tip 2: Avoid close contact with people who have TB.
If you are in close contact with someone who has TB, you should get tested for TB and take medication to prevent TB if you are at high risk of developing the disease.
Tip 3: Get tested for TB if you have symptoms.
If you have symptoms of TB, such as a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue, you should get tested for TB. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Tip 4: Take your medication as prescribed.
If you are diagnosed with TB, it is important to take your medication as prescribed. Treatment for TB can be lengthy and complex, but it is essential to prevent serious complications and death.
Tip 5: Follow your doctor's instructions.
Your doctor will provide you with instructions on how to prevent and manage WPD TB. It is important to follow your doctor's instructions carefully to help prevent serious complications.
Summary: WPD TB is a serious disease, but it can be prevented and managed with early diagnosis and treatment. By following these tips, you can help to protect yourself from WPD TB.
Next steps: If you have any questions about WPD TB, please speak to your doctor or other healthcare provider.
Conclusion
WPD TB is a serious type of tuberculosis that can have serious consequences if it is not diagnosed and treated promptly. However, with early diagnosis and treatment, most people with WPD TB can be cured.
There are several things that can be done to prevent and manage WPD TB, including getting vaccinated against TB, avoiding close contact with people who have TB, getting tested for TB if you have symptoms, and taking your medication as prescribed. By following these tips, you can help to protect yourself from WPD TB.
Legendary Mexican Pozole: A Culinary Journey Through History
Ultimate Fortnite DBV Guide: Unlocking The Secrets Of The Epic Weapon
Oda Congratulates Himself On Achieving Billionaire Status By 2024