A Comprehensive Guide To Christian Denominations In Europe
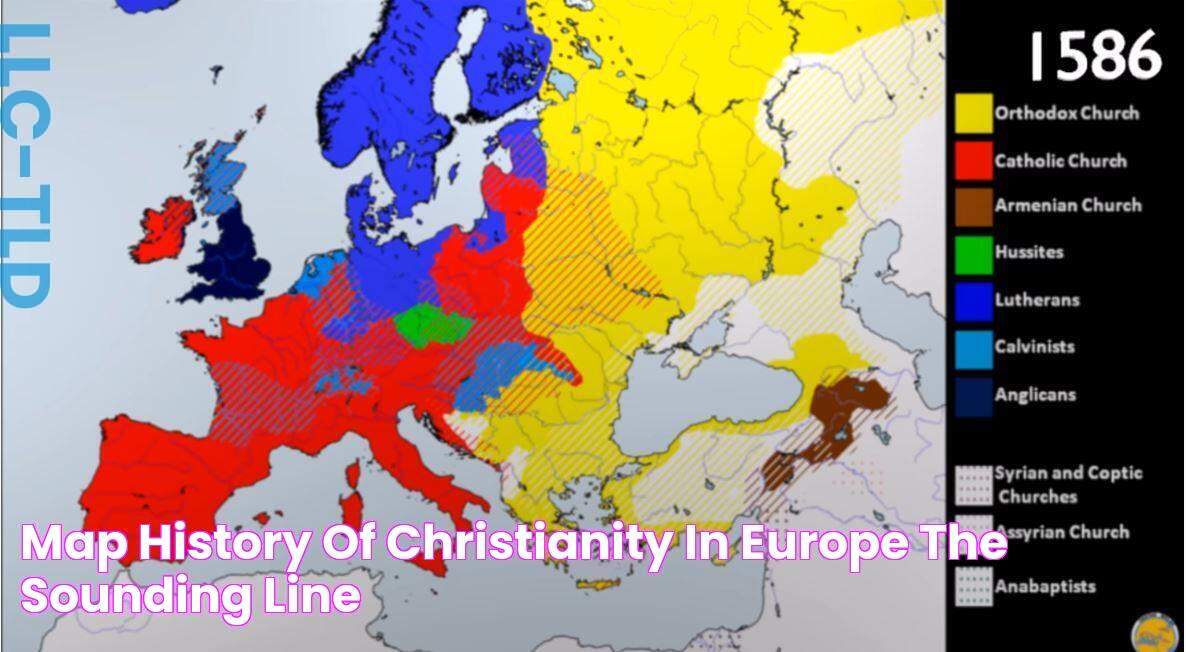
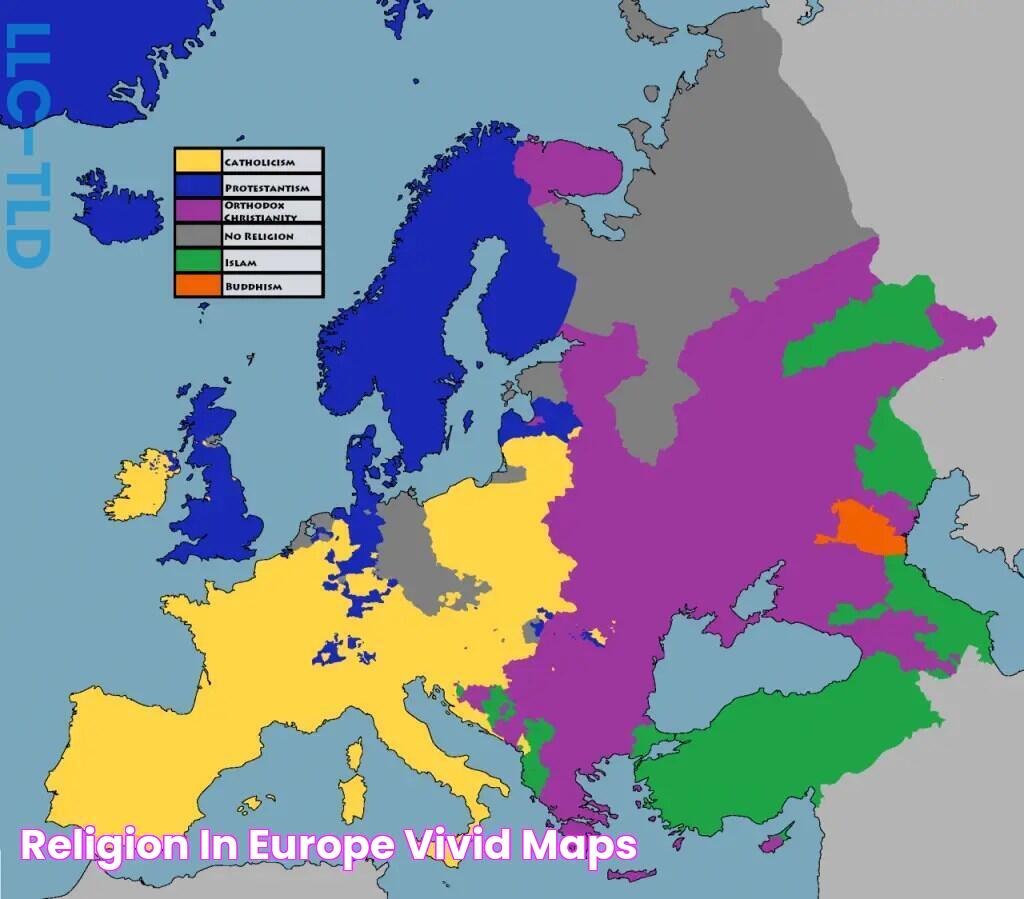
Christianity is the most widely practiced religion in Europe, with a diverse range of denominations. Christian denominations in Europe include Catholicism, Protestantism, and Eastern Orthodoxy, each with its own unique history, beliefs, and practices.
The presence of multiple Christian denominations in Europe has contributed to the continent's rich cultural and religious heritage. Different denominations have played significant roles in shaping European history, art, and architecture. They have also influenced social and political developments, fostering both unity and division at various times.
To fully understand the religious landscape of Europe, it is essential to explore the diverse Christian denominations that have shaped its history and continue to influence its present-day societies.
Read also:The Definitive Guide To Leonardo Dicaprios Age From Boyhood To Stardom
Christian Denominations in Europe
Understanding the diverse Christian denominations in Europe is crucial for grasping the continent's religious landscape and its historical and cultural heritage. Here are eight key aspects to consider:
- Catholicism
- Orthodoxy
- Protestantism
- Anglicanism
- Lutheranism
- Calvinism
- Baptism
- Pentecostalism
These denominations reflect a wide range of beliefs and practices, from the centralized authority of the Catholic Church to the more decentralized and individualistic nature of Protestantism. They have influenced European history, art, architecture, and social and political developments, contributing to both unity and division at various times.
For instance, the Catholic Church played a central role in the development of medieval European civilization, while the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century led to religious wars and political upheavals. Today, Christian denominations continue to shape European societies, providing spiritual guidance, social services, and contributing to interfaith dialogue and cooperation.
1. Catholicism
Catholicism is the largest Christian denomination in Europe, with approximately 280 million members. It is a diverse and complex tradition with a rich history and a profound influence on European culture, society, and politics.
The Catholic Church traces its origins to the early Christian communities founded by Jesus's apostles. Over the centuries, it has developed a distinctive set of beliefs and practices, including the belief in the Trinity, the sacraments, and the authority of the Pope as the successor of Peter.
Catholicism has played a central role in shaping the history of Europe. It was the dominant religion of the Roman Empire and played a key role in the development of medieval European civilization. The Catholic Church was also a major patron of the arts and sciences, and its monasteries were centers of learning and culture.
Read also:Uncover Taylor Swifts Towering Height All The Details
Today, Catholicism continues to be a major force in European society. It provides spiritual guidance and social services to millions of people, and it is a vocal advocate for social justice and peace.
Overall, Catholicism is a vital part of the Christian denominations in Europe. It has a long and rich history, and it continues to play an important role in the lives of millions of Europeans.2. Orthodoxy
Orthodoxy is the second largest Christian denomination in Europe, with approximately 150 million members. It is a diverse and complex tradition with a rich history and a profound influence on European culture, society, and politics.
Orthodoxy traces its origins to the early Christian communities founded by Jesus's apostles. Over the centuries, it has developed a distinctive set of beliefs and practices, including the belief in the Trinity, the sacraments, and the authority of the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople as the spiritual leader of the Orthodox Church.
Orthodoxy played a central role in the development of Byzantine civilization and the spread of Christianity to Eastern Europe. It was the dominant religion of the Russian Empire and played a key role in the development of Russian culture and society.
Today, Orthodoxy continues to be a major force in European society. It provides spiritual guidance and social services to millions of people, and it is a vocal advocate for social justice and peace.
Overall, Orthodoxy is a vital part of the Christian denominations in Europe. It has a long and rich history, and it continues to play an important role in the lives of millions of Europeans.
3. Protestantism
Protestantism is a major branch of Christianity that emerged in Europe during the 16th century. It is a diverse and complex tradition with a rich history and a profound influence on European culture, society, and politics.
The Protestant Reformation began in 1517 when Martin Luther, a German monk, challenged the authority of the Catholic Church. Luther argued that salvation could only be achieved through faith in Jesus Christ, and he rejected the Catholic Church's teachings on indulgences, purgatory, and the authority of the Pope.
Luther's ideas quickly spread throughout Europe, and soon other reformers, such as John Calvin and Andreas Karlstadt, emerged. These reformers established new Protestant churches, and by the end of the 16th century, Protestantism had become a major force in European Christianity.
Protestantism had a profound impact on European history. It led to religious wars and political upheavals, and it contributed to the development of new forms of government and society. Protestantism also had a major impact on European culture, art, and literature.
Today, Protestantism is one of the largest Christian denominations in Europe. It is a diverse tradition with a wide range of beliefs and practices. Protestant churches play a major role in the lives of millions of Europeans, and they continue to be a force for social justice and peace.
4. Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a major branch of Christianity that originated in England in the 16th century. It is a distinctive tradition with a rich history and a profound influence on European culture, society, and politics.
- Origins and History
Anglicanism emerged during the English Reformation, when King Henry VIII broke with the Catholic Church and established the Church of England. The Anglican Church adopted some Protestant beliefs and practices, but it retained many Catholic traditions. This unique blend of Protestant and Catholic elements has shaped Anglicanism's distinctive identity.
- Beliefs and Practices
Anglicans share many of the core beliefs of other Christians, such as the Trinity, the divinity of Jesus Christ, and the importance of the Bible. However, Anglicans also have some distinctive beliefs and practices, such as the emphasis on the Book of Common Prayer and the role of bishops in the church.
- Structure and Governance
The Anglican Communion is a worldwide fellowship of churches that share the Anglican tradition. The Archbishop of Canterbury is the spiritual leader of the Anglican Communion, but each national church is autonomous and governs itself.
- Influence on European Culture and Society
Anglicanism has had a profound influence on European culture and society. Anglican churches have played a major role in education, healthcare, and social welfare. Anglican theologians and scholars have made significant contributions to philosophy, literature, and the arts.
In conclusion, Anglicanism is a vital part of the Christian denominations in Europe. It is a distinctive tradition with a rich history and a profound influence on European culture, society, and politics.
5. Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the major branches of Protestantism that emerged during the Reformation in the 16th century. It is named after Martin Luther, a German theologian and reformer who challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and played a key role in the development of Lutheran theology. Lutheranism has had a profound impact on the religious landscape of Europe, and it continues to be a significant force in Christianity today.
- Core Beliefs:
Lutheranism emphasizes the authority of Scripture and the importance of faith in Jesus Christ for salvation. Lutherans believe that salvation is a gift from God that cannot be earned through good works. They also emphasize the importance of the sacraments, such as baptism and communion, as means of grace.
- Church Governance:
Lutheran churches are typically governed by a system of bishops and synods. Bishops are ordained ministers who oversee a diocese or region, and synods are gatherings of clergy and lay representatives who make decisions on matters of doctrine and church policy.
- Influence on European Culture:
Lutheranism has had a significant impact on European culture and society. Lutheran theologians and scholars have made major contributions to philosophy, literature, and the arts. Lutheran churches have also played a key role in the development of education and social welfare programs.
- Global Reach:
While Lutheranism originated in Europe, it has spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Africa, and Asia. Today, there are approximately 75 million Lutherans around the world.
In conclusion, Lutheranism is a vibrant and diverse branch of Christianity that has played a major role in shaping the religious landscape of Europe. Its emphasis on Scripture, faith, and grace has had a profound impact on the lives of millions of people around the world.
6. Calvinism
Calvinism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged in Europe during the 16th century. It is named after John Calvin, a French theologian and reformer who developed a systematic theology that emphasized the sovereignty of God and the importance of predestination. Calvinism has had a profound impact on the development of Christian denominations in Europe, and it continues to be a significant force in Christianity today.
One of the key tenets of Calvinism is the belief in the sovereignty of God. Calvinists believe that God is in control of all things, and that he has predetermined everything that will happen. This belief has led to a strong emphasis on the importance of God's grace in salvation. Calvinists believe that salvation is a gift from God that cannot be earned through good works.
Another important aspect of Calvinism is the emphasis on predestination. Calvinists believe that God has chosen some people to be saved and others to be damned. This belief has led to a strong emphasis on the importance of living a holy life. Calvinists believe that those who are saved will be able to live a life that is pleasing to God, and that they will be rewarded in heaven.
Calvinism has had a significant impact on the development of Christian denominations in Europe. Calvinist churches have been established in many countries, and they continue to play a major role in the lives of millions of people. Calvinism has also had a major impact on the development of Protestant theology, and its ideas have been influential in many other Christian traditions.
In conclusion, Calvinism is a major branch of Protestantism that has had a profound impact on the development of Christian denominations in Europe. Its emphasis on the sovereignty of God and the importance of predestination has led to a strong emphasis on the importance of God's grace in salvation and the importance of living a holy life. Calvinism continues to be a significant force in Christianity today, and its ideas continue to influence the lives of millions of people around the world.
7. Baptism
Baptism is a Christian rite of initiation that symbolizes the recipient's faith in Jesus Christ and incorporation into the Christian community. It is one of the most important sacraments in Christianity, and it is practiced by all major Christian denominations in Europe.
- Infant Baptism
Infant baptism is the practice of baptizing infants shortly after birth. It is the most common form of baptism in Europe, and it is practiced by both Catholic and Protestant denominations. Infant baptism is based on the belief that baptism is a sacrament that washes away original sin and brings the recipient into the covenant with God.
- Believer's Baptism
Believer's baptism is the practice of baptizing only those who have made a conscious decision to follow Jesus Christ. It is most common among Baptist and Pentecostal denominations. Believer's baptism is based on the belief that baptism is a symbol of a person's faith in Jesus Christ, and that it should only be practiced by those who have made a personal commitment to follow him.
- Immersion Baptism
Immersion baptism is the practice of baptizing someone by fully immersing them in water. It is the most common form of baptism among Baptist and Pentecostal denominations. Immersion baptism is based on the belief that it is the most biblical form of baptism, and that it best symbolizes the death, burial, and resurrection of Jesus Christ.
- Sprinkling Baptism
Sprinkling baptism is the practice of baptizing someone by sprinkling water on their head. It is the most common form of baptism among Catholic and Lutheran denominations. Sprinkling baptism is based on the belief that it is a valid form of baptism, and that it is more practical than immersion baptism.
The practice of baptism varies widely among Christian denominations in Europe. However, all denominations agree that baptism is an important sacrament that symbolizes the recipient's faith in Jesus Christ and incorporation into the Christian community.
8. Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism is a major branch of Christianity that emerged in the early 20th century. It is characterized by an emphasis on the baptism of the Holy Spirit, which is believed to empower believers with spiritual gifts such as speaking in tongues, prophecy, and healing.
- Origins and History
Pentecostalism originated in the United States in the early 1900s. It quickly spread to Europe, where it gained a foothold in many countries. Today, there are an estimated 600,000 Pentecostals in Europe.
- Beliefs and Practices
Pentecostals believe that the baptism of the Holy Spirit is a second experience that follows salvation. They also believe in the importance of spiritual gifts, which they believe are given to believers to build up the church.
- Influence on European Christianity
Pentecostalism has had a significant influence on European Christianity. Pentecostal churches have been established in many countries, and they are playing a growing role in the lives of European Christians.
- Challenges and Opportunities
Pentecostalism faces a number of challenges in Europe, including the secularization of society and the rise of other charismatic movements. However, Pentecostals are also finding new opportunities to share their faith, such as through social media and mission work.
In conclusion, Pentecostalism is a vibrant and growing branch of Christianity in Europe. Pentecostals are passionate about their faith, and they are committed to sharing their beliefs with others. Pentecostalism is likely to continue to play a significant role in the religious landscape of Europe for many years to come.
FAQs on Christian Denominations in Europe
This section addresses frequently asked questions about Christian denominations in Europe, providing concise and informative answers to common concerns or misconceptions.
Question 1: What are the major Christian denominations in Europe?
The major Christian denominations in Europe include Catholicism, Orthodoxy, Protestantism, Anglicanism, Lutheranism, Calvinism, Baptism, and Pentecostalism.
Question 2: What are the key differences between these denominations?
The key differences between these denominations lie in their beliefs, practices, and ecclesiastical structures. For example, Catholicism emphasizes the authority of the Pope and the importance of sacraments, while Protestantism emphasizes the authority of the Bible and the importance of faith.
Question 3: How have Christian denominations influenced European history and culture?
Christian denominations have played a significant role in shaping European history and culture. They have influenced political systems, social structures, art, architecture, and education. For example, the Catholic Church played a major role in the development of medieval European civilization.
Question 4: Are there any ecumenical efforts among Christian denominations in Europe?
Yes, there are several ecumenical organizations and initiatives that promote dialogue and cooperation among Christian denominations in Europe. These efforts aim to foster greater understanding, unity, and collaboration.
Question 5: What are the challenges facing Christian denominations in Europe today?
Christian denominations in Europe face challenges such as secularization, declining church attendance, and the rise of religious pluralism. They are also grappling with issues related to social justice, interfaith dialogue, and the role of women in church leadership.
Question 6: What is the future of Christian denominations in Europe?
The future of Christian denominations in Europe is uncertain. However, they continue to play an important role in the lives of many Europeans and are likely to continue to do so in the years to come.
Summary: Christian denominations in Europe represent a diverse and complex landscape of beliefs, practices, and historical influences. Understanding their differences and their impact on European history and culture is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the continent's religious heritage.
Transition: This concludes our exploration of Christian denominations in Europe. In the next section, we will delve into the specific beliefs and practices of each denomination.
Understanding Christian Denominations in Europe
To delve deeper into the intricacies of Christian denominations in Europe, consider these informative tips:
Tip 1: Explore Historical Context: Trace the historical roots of each denomination to grasp how they emerged, evolved, and shaped European history.
Tip 2: Examine Core Beliefs: Study the fundamental doctrines and theological tenets that distinguish one denomination from another, such as views on salvation, sacraments, and church authority.
Tip 3: Analyze Liturgical Practices: Compare the liturgical practices, rituals, and worship styles employed by different denominations, noting their similarities and variations.
Tip 4: Consider Cultural Impact: Investigate the influence of Christian denominations on European culture, including their contributions to art, architecture, music, and social welfare.
Tip 5: Engage in Interfaith Dialogue: Foster dialogue and understanding among different Christian denominations and with other faith traditions to promote ecumenical cooperation and bridge divides.
Tip 6: Respect Diversity: Recognize and appreciate the diversity of Christian denominations in Europe, valuing their unique perspectives and contributions to the religious landscape.
Tip 7: Seek Scholarly Resources: Consult reputable academic sources, such as books, journals, and online databases, to gain in-depth knowledge and nuanced insights.
Tip 8: Visit Historical Sites: Immerse yourself in the history and heritage of Christian denominations by visiting churches, cathedrals, and other significant religious sites.
By following these tips, you will gain a deeper understanding of the diverse Christian denominations in Europe, their beliefs, practices, and profound impact on the continent's history and culture.
Conclusion: Understanding Christian denominations in Europe is not merely an academic pursuit but a journey of discovery that enriches our appreciation for the complexities of faith, history, and human experience.
Conclusion
This exploration of Christian denominations in Europe has provided a comprehensive overview of the diverse and intricate religious landscape of the continent. From the historical roots and core beliefs of each denomination to their liturgical practices and cultural impact, we have gained a deeper understanding of the ways in which Christianity has shaped European history and society.
As we move forward, it is essential to continue fostering interfaith dialogue and promoting ecumenical cooperation to bridge divides and cultivate mutual understanding. By valuing the diversity of Christian denominations in Europe and engaging in respectful and informed discussions, we can enrich our appreciation for the complexities of faith and its profound influence on our shared human experience.
Custom-Crafted Crown Victorias: Unveiling The Pinnacle Of Personalized Luxury
Circle Surrogacy Reviews: A Comprehensive Guide
Understand The True Meaning Of "GGG" In Gaming: An Ultimate Guide